The Biological Effects of Physical Activity on Aging: How Exercise Reduces Age-Related Diseases and Enhances Longevity

The Role of Physical Exercise in Aging :
Physical exercise plays a fundamental role in aging by influencing various biological processes. It acts as a shield against many age-related chronic diseases while also contributing to longevity and a better quality of life. This phenomenon can be understood through several biological mechanisms at the cellular, molecular, and physiological levels.
Impact on Health and Aging :
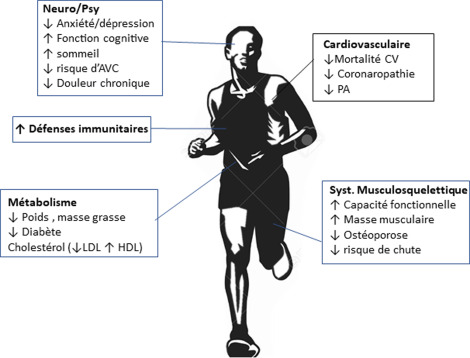
Physical activity brings beneficial changes to the body, improving muscle, cardiovascular, and metabolic functions, as well as bone health, sleep, immunity, and psychological well-being. These adaptations enhance aerobic capacity and muscle strength, which are linked to lower mortality. For instance, increasing VO2max by 3.5 mL/kg/min can reduce mortality by 12%. The effects depend on the type, context, and intensity of exercise. These benefits are seen at all ages, but are particularly important for older adults, helping to slow aging by reducing cardiovascular risks and combating sarcopenia.
Discover more
Practical Tips to Incorporate Exercise into Your Daily Life :
Start gradually:
If you're not used to exercising, begin with short walks or low-impact activities.
Mix up your exercises:
Alternate between walking, swimming, yoga, cycling, and strength training to stimulate different body systems.
Listen to your body:
Be mindful not to overexert yourself. Pay attention to your body’s signals and adjust the intensity as needed.

The Impact of Exercise on Cellular Health Preservation and Age-Related Disease Reduction
Regular physical activity plays a key role in reducing the risk of age-related chronic diseases like heart conditions, diabetes, and osteoarthritis by improving circulation, strengthening the immune system, and maintaining a healthy weight. It also helps preserve muscle and bone mass, preventing fractures and falls, especially through resistance exercises and balance training. Exercise stimulates brain health by promoting neurotrophic factors, reducing the risk of cognitive decline and dementia. Additionally, physical activity boosts mood and reduces stress by releasing endorphins, improving sleep quality, and combating social isolation. By enhancing physical, cognitive, and emotional well-being, exercise is crucial for healthier aging.

